WHAT IS PILATES?
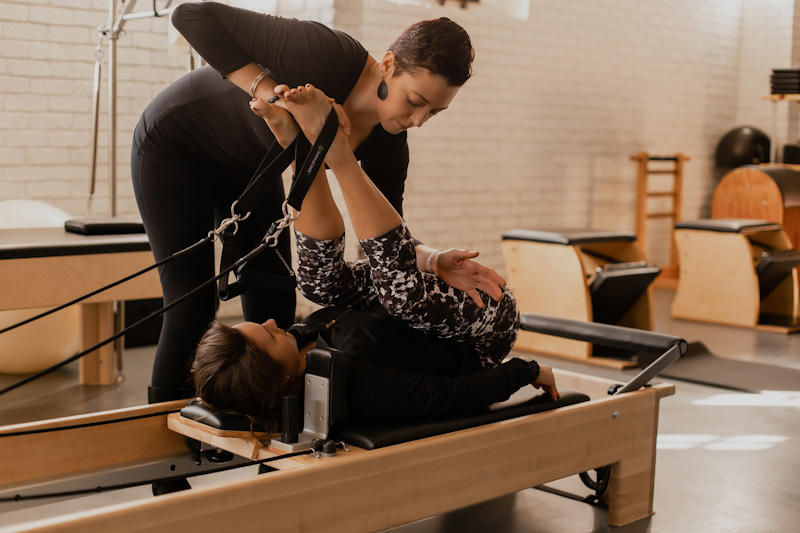
Originally called “Contrology”, Pilates is a physical strength and fitness system developed in the early 20th century by German born Joseph Pilates, after whom the system is now named. Joseph Pilates was sickly and weak as a child and decided from an early age to improve his wellbeing through exercise. To that end, he started and practiced body building, gymnastics and many other forms of movement and exercise. During World War 1, Pilates was interned in Britain as a German alien, where he worked as a nurse. It was during this time that he started developing the Contrology exercise system as it was then known. Attaching springs to hospital beds and utilising the resistance this provided to movement, allowed patients to start building up their muscle strength again. The most well-known piece of equipment based on the hospital bed, is the Reformer. Later, upon moving to the US, Pilates became a professional boxer and worked with the boxing clubs in New York while continuing to develop his exercise system.
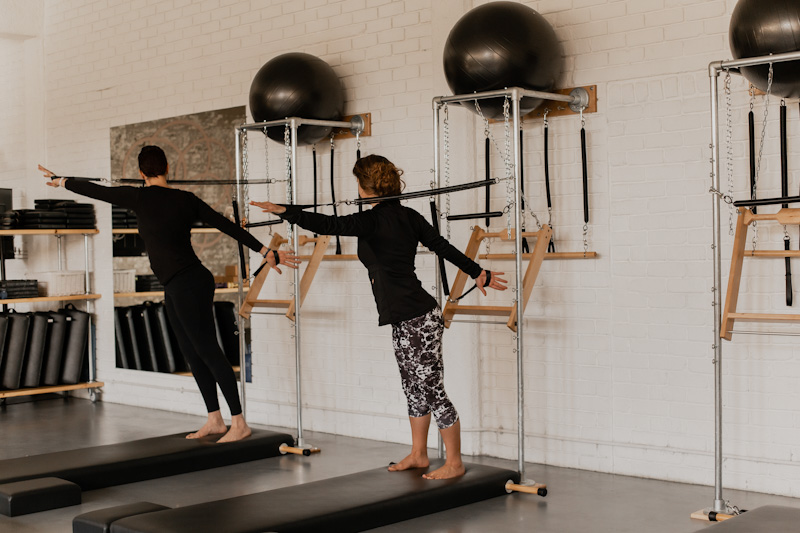
Pilates as an exercise regime, is low impact and works on strengthening the ‘powerhouse’, better known as the core, and from there the body as a whole. Joseph Pilates also developed other equipment including the Wunda Chair, Pilates Mat and Cadillac to name but a few. The goal is to improve movement as quickly and efficiently as possible, which encompasses both strength and flexibility training.
There are various types of Pilates taught throughout the world including, but not limited to, Classical Pilates, Stott Pilates and BASI Pilates. All types of Pilates have the same foundation due to the origin of Pilates having such a specific source. Over the years, the different types of Pilates have added to or developed their own focal point. Some have included new/more equipment, others have developed to be more rehab based while Classical Pilates focuses on maintaining the Pilates system as close as possible to how it was originally developed by Pilates himself.
Pilates is an exercise system which can and should be geared to the strengths and abilities of the clients, which makes it accessible to elite athletes and amateurs alike.
WHAT IS YOGA?
Yoga is a way of creating union between all the parts of yourself, physical, mental, spiritual, known and unknown, to reach a state of ‘enlightenment’.
Yoga is one of the six Hindu philosophical traditions which originated in Ancient India and is the Sanskrit word for ‘Union’, loosely relating to the union between body, mind and spirit. For the purposes of this post we will focus on modern/western yoga, while appreciating that yoga is an age-old tradition with many different branches and schools of philosophy
Yoga consists of several different types, but the earliest forms of yoga had little to do with the physical body and poses. The focus was more on meditation and breathing, amongst other practices, in order to achieve the enlightened state. Modern yoga falls under the umbrella of ‘Hatha’ meaning force, where the focus is largely on the body and body postures known as ‘asana’ and utilises the body as the vehicle to enlightenment. The earliest yogic writings date back to approximately 1500 BCE, however yoga asana only started appearing in the texts from the 1400’s. This means yoga as it is known in the western world today, is relatively new to yogic tradition. According to the Yoga Sutra’s of Patanjali, one of the philosophical texts used in yoga, there are 8 elements or steps that make up the path of yoga and enlightenment. These are
- Yamas – moral codes or commandments
- Niyamas – personal duties or obeservances
- Asana – physical postures
- Pranayama – breath and energy regulation
- Pratyahara – withdrawal of the senses
- Dharana – concentration
- Dhyana – meditation
- Samadhi – bliss or superior consciousness
Asana is the third of the eight limbs, which indicates that while asana is not the only step in the path to enlightenment, it is very definitely one of the steps. This lineage of Hatha yoga which is so dominant in modern day yoga can then be further divided into many different styles which include Ashtanga, Vinyasa, Iyengar, Synergy and Hatha (the style and different to the umbrella term used to describe postural yoga). For more detail on how the various styles of yoga differ, Click here where Stepfanie Romine details the 13 most popular styles of yoga.